Contents
Get started
Learn how to start creating 2D apps in Ruby
Set up your Ruby environment
Ruby 2D makes use of low-level graphics and hardware, so you’ll need a Ruby environment that can build native extensions. If you’re new to Ruby and need some help, check out these guides: macOS, Windows, and Linux.
On Linux, you’ll need to install a few packages before installing the gem, see the instructions here.
Install the gem
Now you’re ready to install the Ruby 2D gem! On your command line, run:
gem install ruby2d
Write your first 2D app
After installing the gem, create a new Ruby script called triangle.rb and add the following two lines.
require 'ruby2d'
show
This is the simplest Ruby 2D application you can write. The require statement adds the Ruby 2D domain-specific language and classes, and the show method tells Ruby 2D to show the empty window. Let’s make this window more interesting by giving it a name and adding a shape. We’ll use the set method to change the title of the window and add a colorful triangle.
require 'ruby2d'
set title: "Hello Triangle"
Triangle.new(
x1: 320, y1: 50,
x2: 540, y2: 430,
x3: 100, y3: 430,
color: ['red', 'green', 'blue']
)
show
Great! Now save your script and run it on the command line using:
ruby triangle.rb
You should see this impressive triangle…
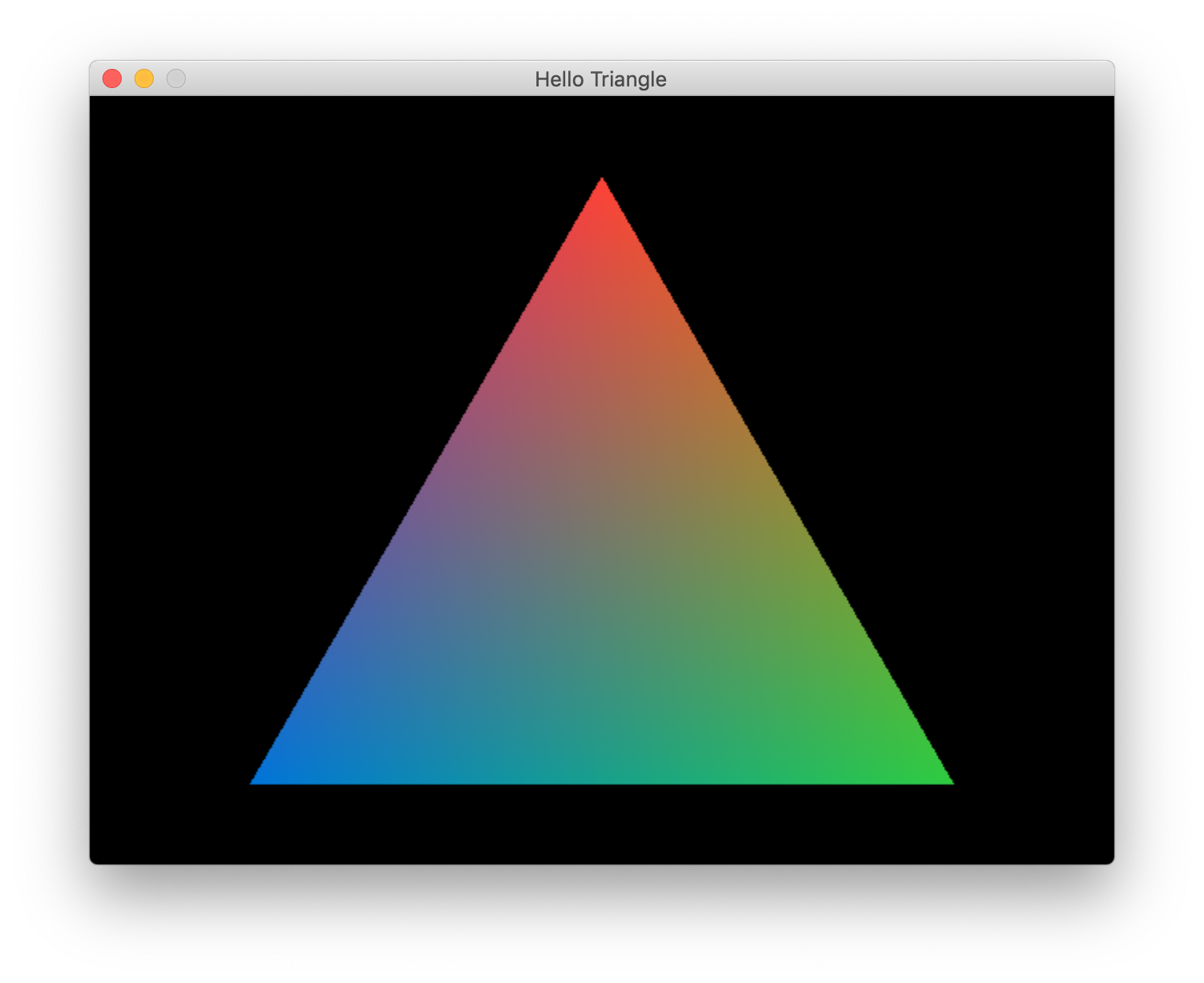
Congrats, you just built your first Ruby 2D app! 🎉
What’s next?
There’s a lot Ruby 2D can do. Check out the showcase to see examples of what you can build. To keep learning, continue to the next topic or select one from the contents menu.